News, Projects, Selected Project
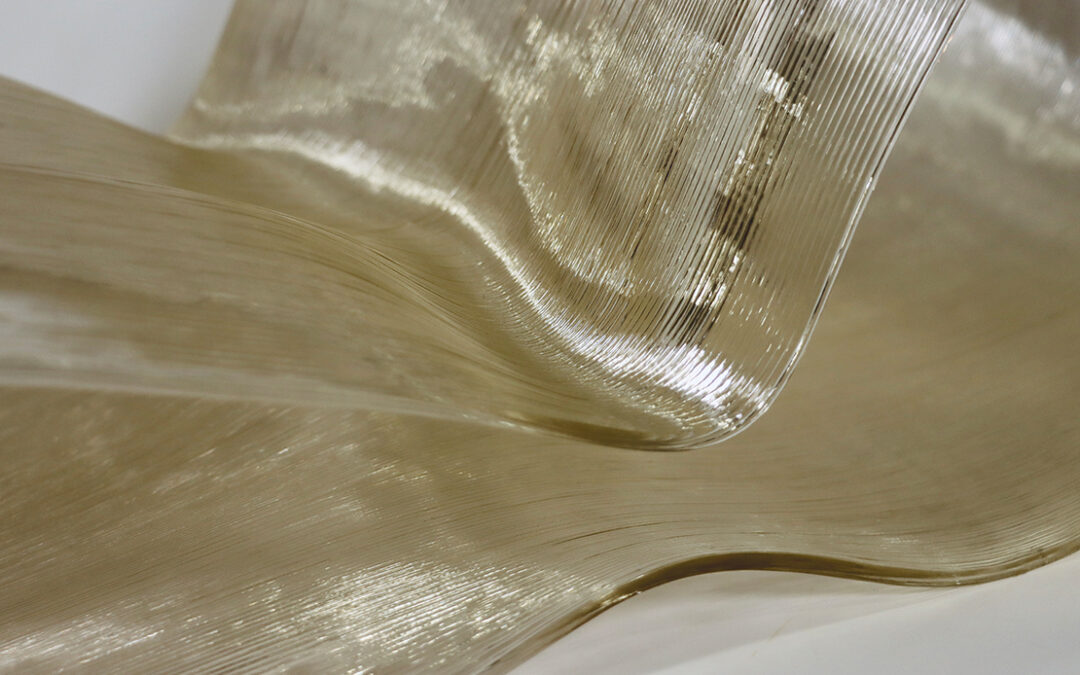
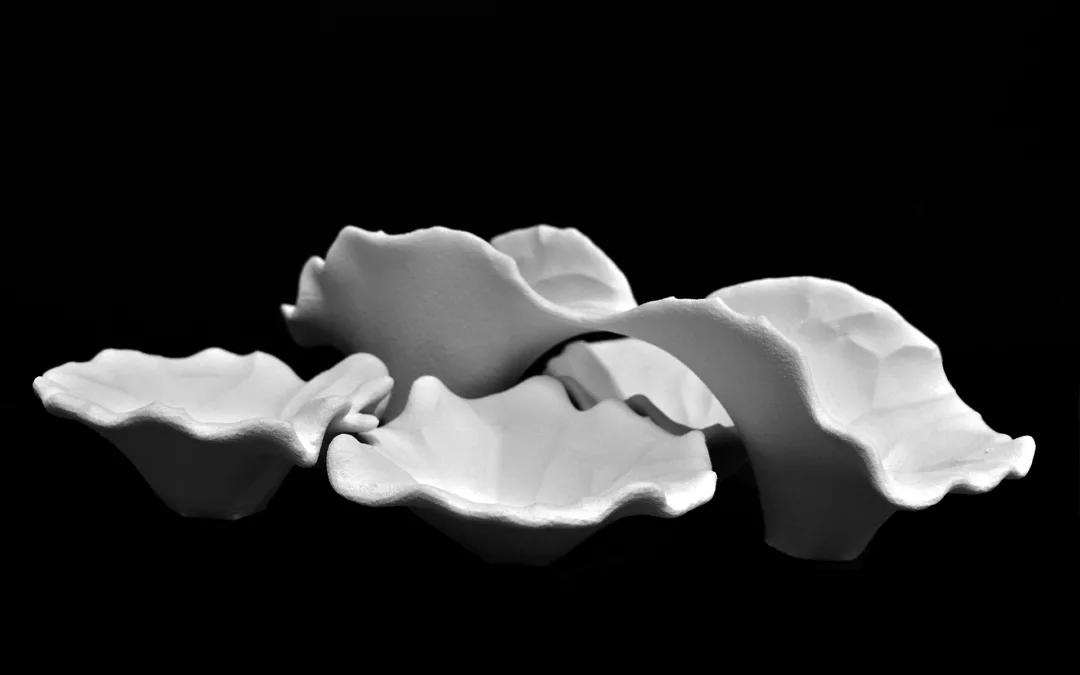
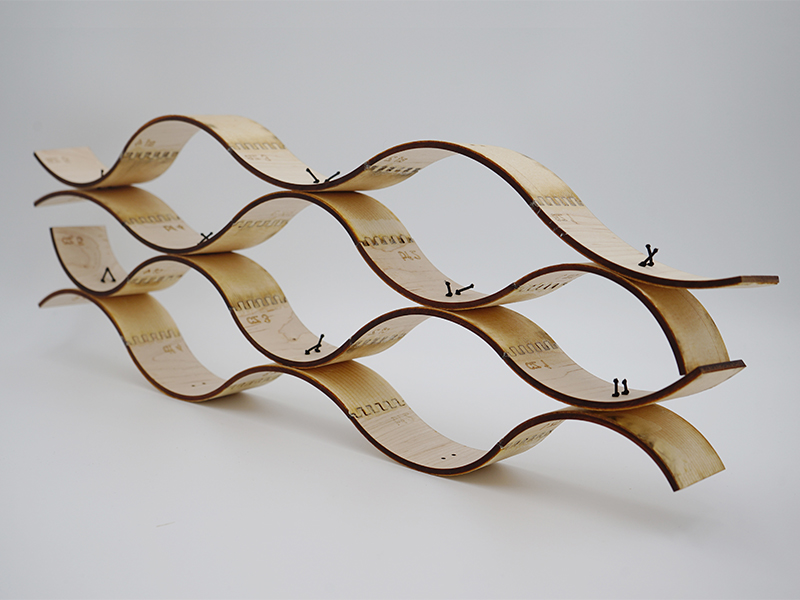
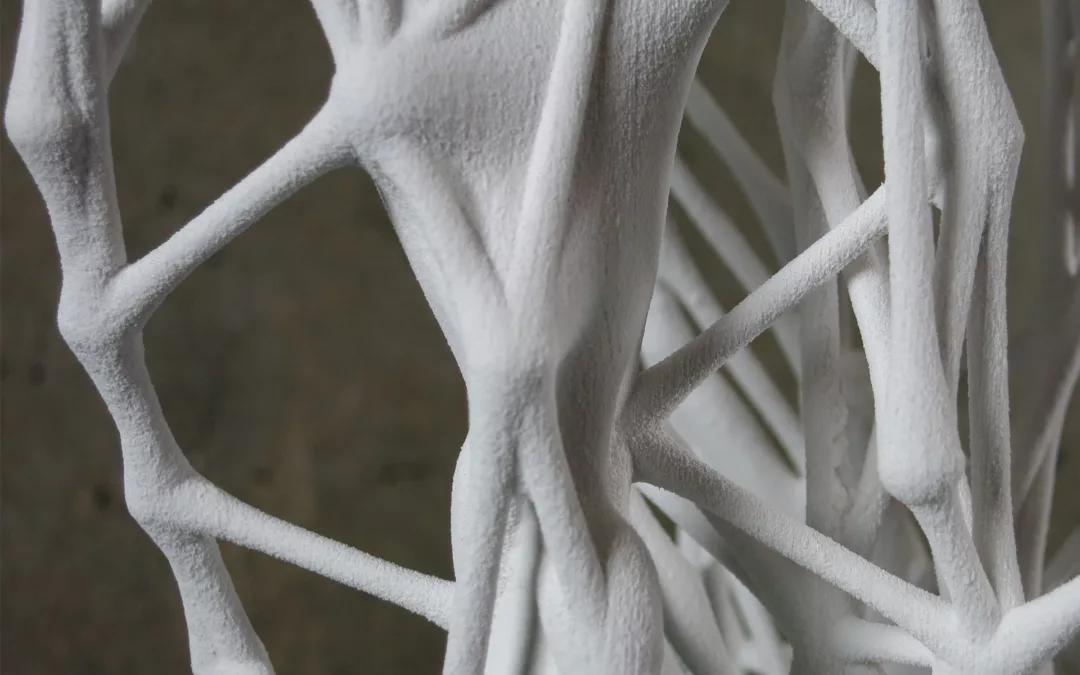
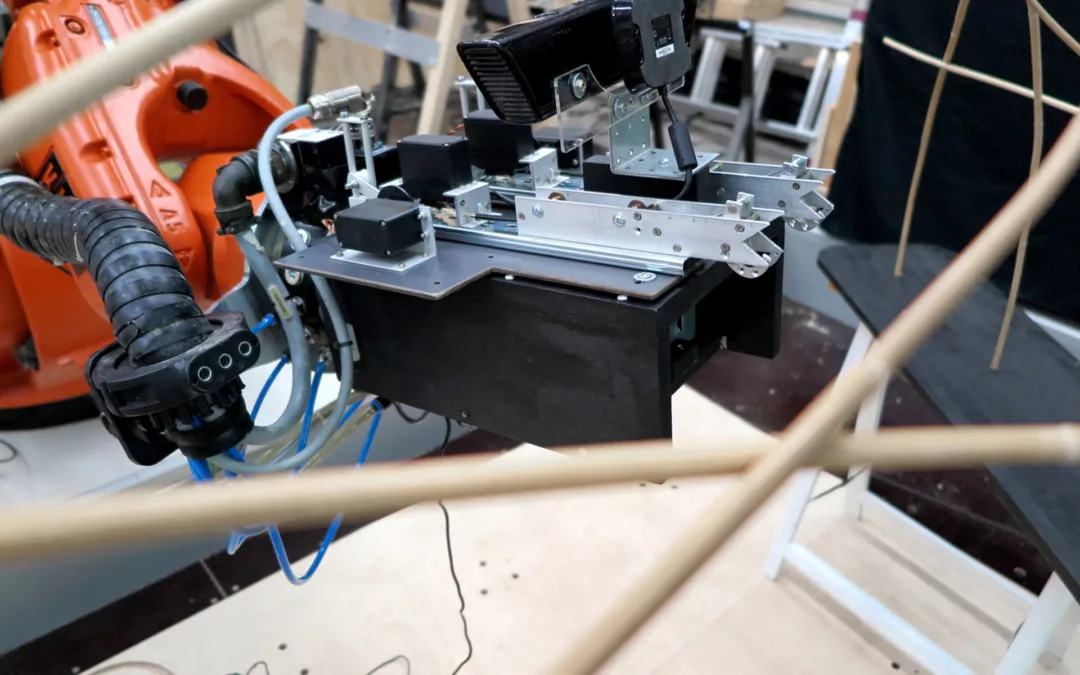
The Co-designing Circular Plastics project was a small initiative. As proof of concept, PI 3D printed a scaled chair (1:2) with an industrial robotic arm.
Development of a Co-designed Circular Interface
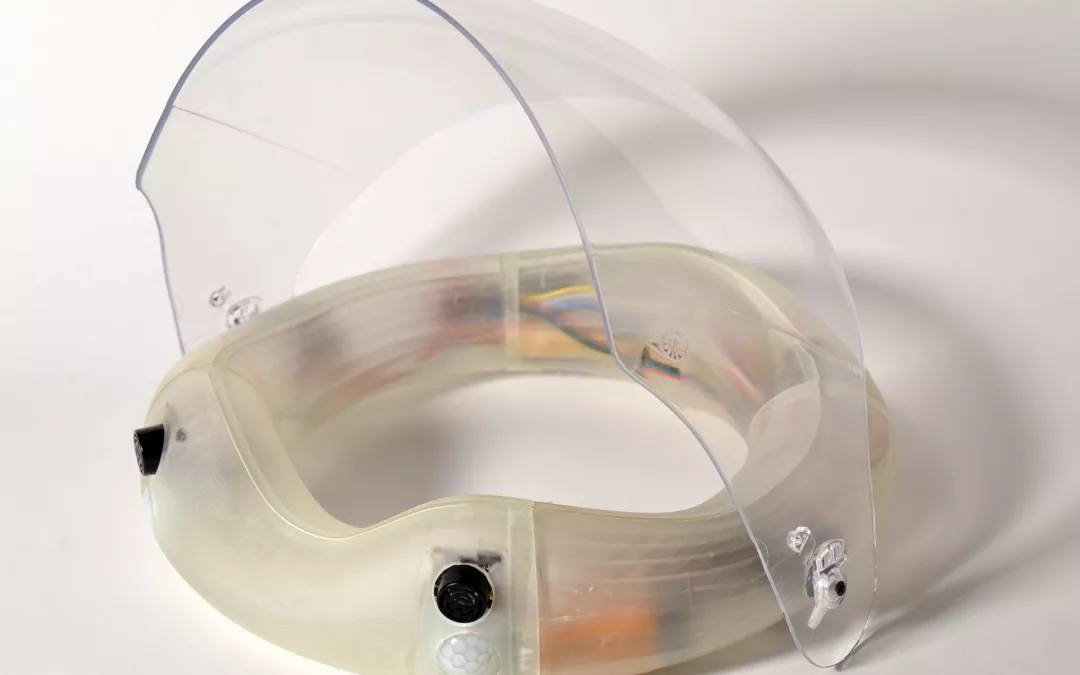
A user interface (UI) was developed to integrate distinct aspects of user-friendly and circular economy.
Implementation of Co-designed Circular Construction
A design-for-fabrication method was developed to integrate material properties and robotic fabrication into consideration. This integrated design method follows the principles of co-designing circular plastics. The process includes the preparation of recycled materials for printing a chair with an industrial robotic arm.
The Result of Co-designed Circular Plastics
A scaled model (1:2) of a chair was designed based on human ergonomics while considering material and fabrication capacities.
Since 2018, PI has developed an advanced technology curriculum that highlights the agency of materials in our built environment. Courses like ARCH5500-Computational design and construction, ARCH5500–Behavioral robotic fabrication, ARCH 5500-Cognitive design and fabrication, and ARCH5500-Robotic additive manufacturing focus on applying advanced technologies in design. This fund supported these ongoing curricula to advance UVA’s position in sustainability for design and construction. It helped students learn a new economic model in design and construction.
Project Funding
This project was funded by the Jefferson Trust.
Related Projects
This project was further developed through additional funding from the Jefferson Trust in Chair No. 7.
Author and Image Credit
Ehsan Baharlou
Image Credit
Ehsan Baharlou, CT .lab, University of Virginia, 2023

Courses, News
Additive Tectonics
“When a structural concept has found its implementation through construction, the visual result will affect us through certain expressive qualities which clearly have something to do with the play of forces and corresponding arrangement of parts in the building, yet cannot be described in terms of construction and structure alone. For these qualities, which are expressive of a relation of form to force, the term tectonic should be reserved.”
— Eduard F. Sekler (1960), “Structure, Construction, Tectonics”, in Structure in Art and in Science.
Description
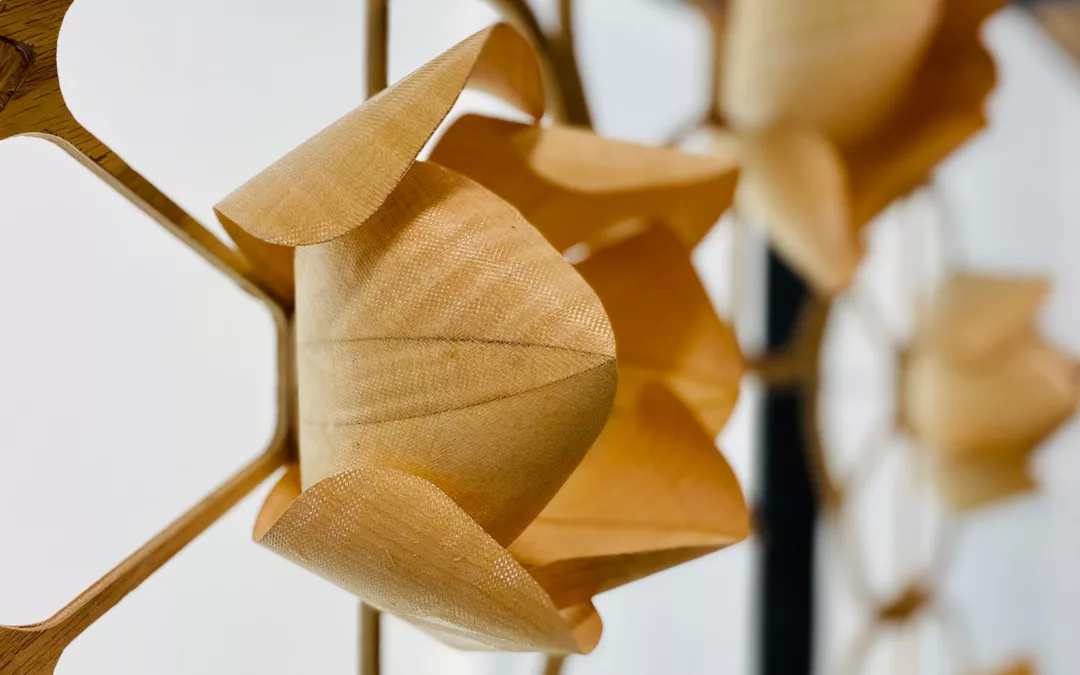
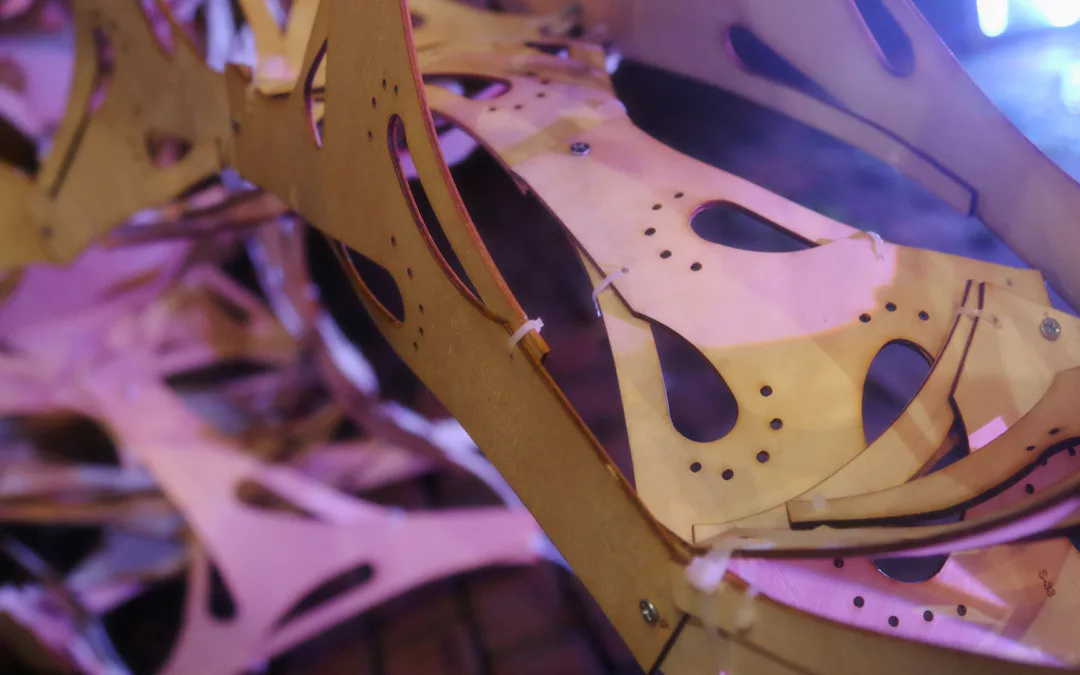
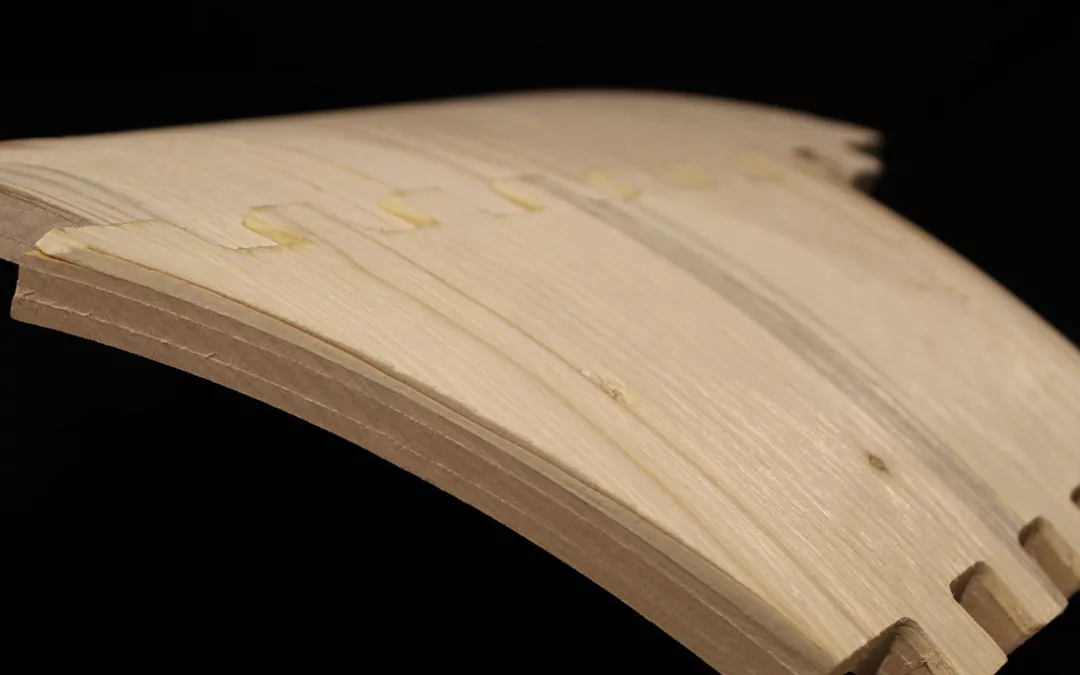
Advances in computational design methods and fabrication techniques provide new possibilities for architectural designers to consider different paradigms for design and making. These paradigms emphasize the relationship between formation and materialization. Through robotic additive manufacturing, designers can construct buildings or building elements quickly.
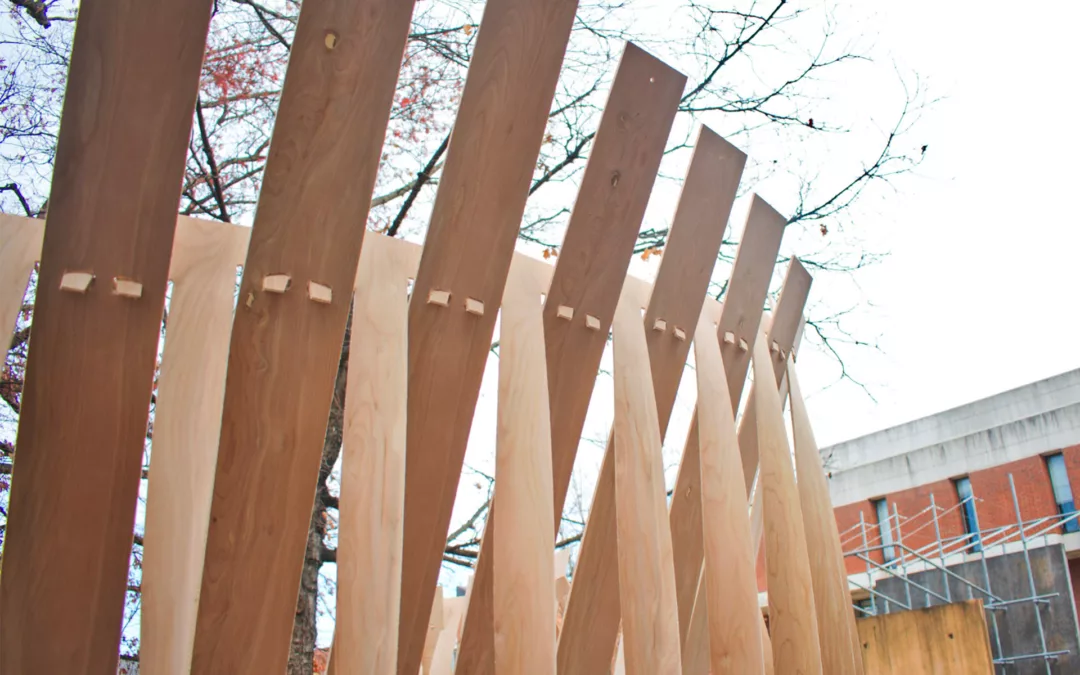
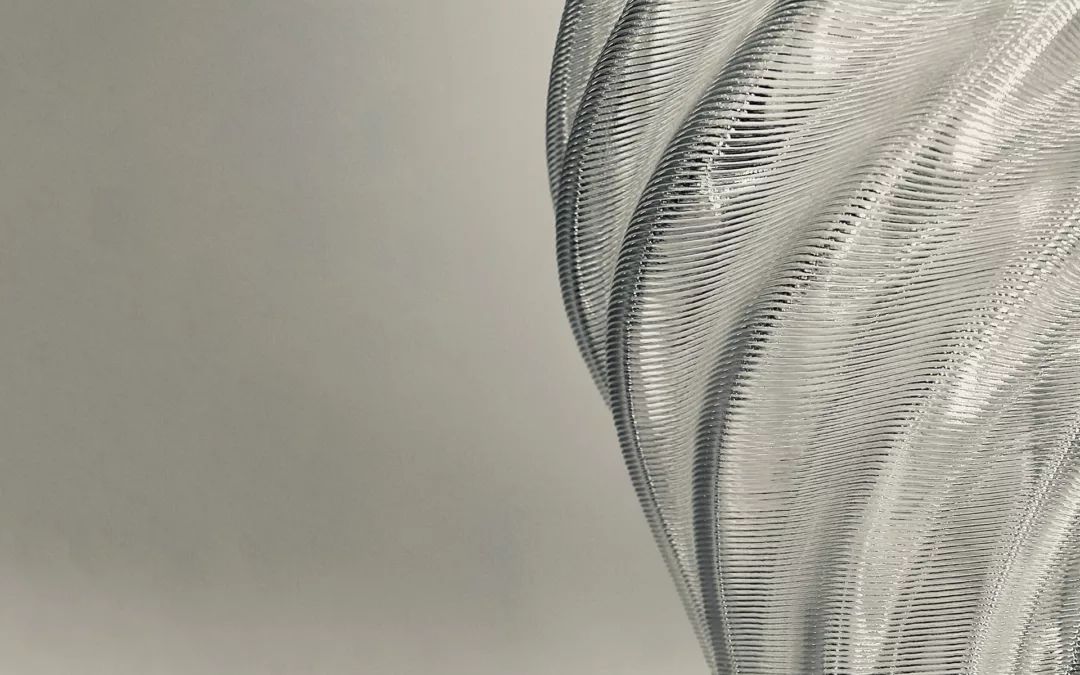
The studio “Additive Tectonics” explored the tectonic expression of additive manufacturing in different architectural contexts, from constructing affordable housing with earth materials to investigating the construction of settlements on other planets. The studio focused on the exploration of such architectural tectonics as an abstracted skin or wall system; a tower or a column as a structural element; a vault or a shell as a roof system; a hut or a shed; or other, new building tectonics. One-to-one structures were designed for the North Terrace at the University of Virginia’s Campbell Hall.
Students explored additive tectonics through three stages. The material system development stage demonstrated various materials—such as bio-based, bio-degradable, or bioplastic materials—and their properties and limitations in additive manufacturing. In computational design development, students considered the material properties and fabrication constraints in prototyping. Finally, robotic additive construction—which can be defined as abstraction, formation, rationalization, and materialization to explore novel tectonics—enabled students to execute their design prototype to examine their design’s tectonic potential in building an architectural element.
A series of integrative workshops supported this studio. Formation workshops introduced Grasshopper as a CAD software that can be used for form generation. Materialization workshops presented students with a numerical-based fabrication process. Students learned to control an industrial robotic arm and 3D-print tectonic prototypes.
Image Credit
E. Baharlou, University of Virginia, 2021.